반응형
Eighth competition following Youhan Lee's curriculum. Regression competition using tabular data.
New York City Taxi Trip Duration
Share code and data to improve ride time predictions
www.kaggle.com
First Kernel: Dynamics of New York city - Animation
- Use K-means clustering to cluster New York into different groups based on location, and analyze the traffic into and out of every cluster as a function of the time along the day
Insight / Summary:
1. Clustering Code Example: cluster New York City based on the pick-up and drop-off points of each taxi ride
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=15, random_state=2, n_init = 10).fit(loc_df)
loc_df['label'] = kmeans.labels_
loc_df = loc_df.sample(200000)
plt.figure(figsize = (10,10))
for label in loc_df.label.unique():
plt.plot(loc_df.longitude[loc_df.label == label],loc_df.latitude[loc_df.label == label],'.', alpha = 0.3, markersize = 0.3)
plt.title('Clusters of New York')
plt.show()
2. Plotting cluster center
fig,ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,10))
for label in loc_df.label.unique():
ax.plot(loc_df.longitude[loc_df.label == label],loc_df.latitude[loc_df.label == label],'.', alpha = 0.4, markersize = 0.1, color = 'gray')
ax.plot(kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,0],kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,1],'o', color = 'r')
ax.annotate(label, (kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,0],kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,1]), color = 'b', fontsize = 20)
ax.set_title('Cluster Centers')
plt.show()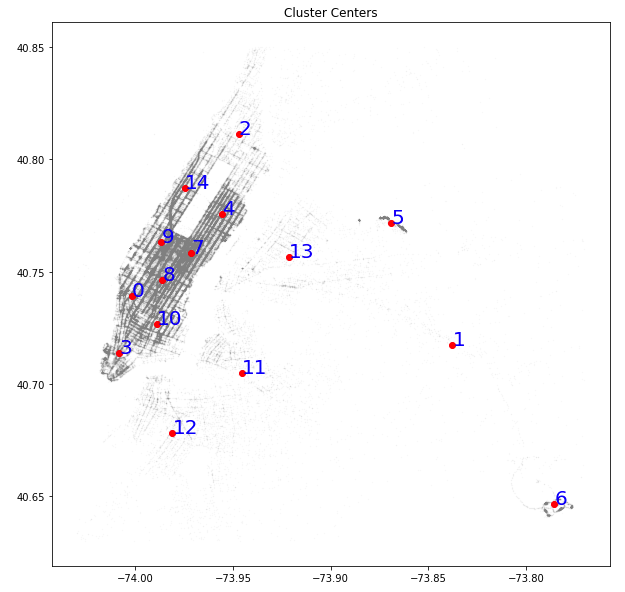
3. Plotting taxi rides from one cluster to another
Absolute traffic:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (10,10))
def animate(hour):
ax.clear()
ax.set_title('Absolute Traffic - Hour ' + str(int(hour)) + ':00')
plt.figure(figsize = (10,10));
for label in loc_df.label.unique():
ax.plot(loc_df.longitude[loc_df.label == label],loc_df.latitude[loc_df.label == label],'.', alpha = 1, markersize = 2, color = 'gray');
ax.plot(kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,0],kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,1],'o', color = 'r');
for label in clusters.label:
for dest_label in clusters.label:
num_of_rides = len(df[(df.pickup_cluster == label) & (df.dropoff_cluster == dest_label) & (df.pickup_hour == hour)])
dist_x = clusters.x[clusters.label == label].values[0] - clusters.x[clusters.label == dest_label].values[0]
dist_y = clusters.y[clusters.label == label].values[0] - clusters.y[clusters.label == dest_label].values[0]
pct = np.true_divide(num_of_rides,len(df))
arr = Arrow(clusters.x[clusters.label == label].values, clusters.y[clusters.label == label].values, -dist_x, -dist_y, edgecolor='white', width = 15*pct)
ax.add_patch(arr)
arr.set_facecolor('g')
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig,animate,sorted(df.pickup_hour.unique()), interval = 1000)
plt.close()
ani.save('animation.gif', writer='imagemagick', fps=2)
filename = 'animation.gif'
video = io.open(filename, 'r+b').read()
encoded = base64.b64encode(video)
HTML(data='''<img src="data:image/gif;base64,{0}" type="gif" />'''.format(encoded.decode('ascii')))Relative traffic:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize = (10,10))
def animate(hour):
ax.clear()
ax.set_title('Relative Traffic - Hour ' + str(int(hour)) + ':00')
plt.figure(figsize = (10,10))
for label in loc_df.label.unique():
ax.plot(loc_df.longitude[loc_df.label == label],loc_df.latitude[loc_df.label == label],'.', alpha = 1, markersize = 2, color = 'gray')
ax.plot(kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,0],kmeans.cluster_centers_[label,1],'o', color = 'r')
for label in clusters.label:
for dest_label in clusters.label:
num_of_rides = len(df[(df.pickup_cluster == label) & (df.dropoff_cluster == dest_label) & (df.pickup_hour == hour)])
dist_x = clusters.x[clusters.label == label].values[0] - clusters.x[clusters.label == dest_label].values[0]
dist_y = clusters.y[clusters.label == label].values[0] - clusters.y[clusters.label == dest_label].values[0]
pct = np.true_divide(num_of_rides,len(df[df.pickup_hour == hour]))
arr = Arrow(clusters.x[clusters.label == label].values, clusters.y[clusters.label == label].values, -dist_x, -dist_y, edgecolor='white', width = pct)
ax.add_patch(arr)
arr.set_facecolor('g')
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig,animate,sorted(df.pickup_hour.unique()), interval = 1000)
plt.close()
ani.save('animation.gif', writer='imagemagick', fps=2)
filename = 'animation.gif'
video = io.open(filename, 'r+b').read()
encoded = base64.b64encode(video)
HTML(data='''<img src="data:image/gif;base64,{0}" type="gif" />'''.format(encoded.decode('ascii')))Second Kernel: EDA + Baseline Model(0.40 RMSE)
- Literally EDA + making baseline model with decent LB.
Insight / Summary:
1. Calculating Haversine Distance using latitude, longitude
def calculateDistance(row):
R=6373.0 # approximate radius of earth in km
pickup_lat=radians(row['pickup_latitude'])
pickup_lon=radians(row['pickup_longitude'])
dropoff_lat=radians(row['dropoff_latitude'])
dropoff_lon=radians(row['dropoff_longitude'])
dlon = dropoff_lon - pickup_lon
dlat = dropoff_lat - pickup_lat
a = sin(dlat / 2)**2 + cos(pickup_lat) * cos(dropoff_lat) * sin(dlon / 2)**2
c = 2 * atan2(sqrt(a), sqrt(1 - a))
distance = R * c
return distance
2. Bearing
- Bearing (also called azimuth) is the angle between the direction of travel and true north, measured clockwise from north. In other words, it tells you which direction you're heading:
- 0° (or 360°) = North
- 90° = East
- 180° = South
- 270° = West
- The formula is: θ = atan2( sin Δλ ⋅ cos φ2 , cos φ1 ⋅ sin φ2 − sin φ1 ⋅ cos φ2 ⋅ cos Δλ ) λ is the longitude
def calculateBearing(lat1,lng1,lat2,lng2):
R = 6371
lng_delta_rad = np.radians(lng2 - lng1)
lat1, lng1, lat2, lng2 = map(np.radians, (lat1, lng1, lat2, lng2))
y = np.sin(lng_delta_rad) * np.cos(lat2)
x = np.cos(lat1) * np.sin(lat2) - np.sin(lat1) * np.cos(lat2) * np.cos(lng_delta_rad)
return np.degrees(np.arctan2(y, x))Third Kernel: Beat the benchmark!
- Similar kernel but XGBoost used.
Believe in your abilities, even when others doubt you. Your belief will carry you through.
- Max Holloway -
반응형
'캐글' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kaggle Study] #11 Credit Card Fraud Detection (0) | 2024.12.03 |
|---|---|
| [Kaggle Study] #10 Zillow Prize: Zillow’s Home Value Prediction (Zestimate) (0) | 2024.11.29 |
| [Kaggle Study] #8 2018 Data Science Bowl (0) | 2024.11.28 |
| [Kaggle Study] #6 Costa Rican Household Poverty Level Prediction (1) | 2024.11.28 |
| [Kaggle Study] #7 TensorFlow Speech Recognition Challenge (0) | 2024.11.27 |